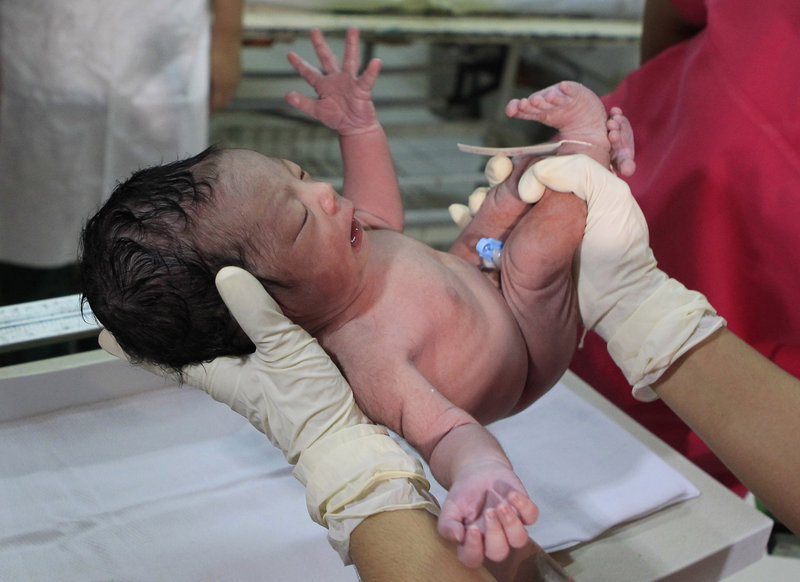
LONDON – A new study in England shows little difference in complications among the babies of women with low-risk pregnancies who delivered in hospitals versus those who gave birth with midwives at home or in birthing centers.
Based on the findings, researchers said women with uncomplicated pregnancies in England should be able to choose where they want to give birth, and one expert said about half of all pregnant women here could potentially safely give birth outside a hospital.
But they sounded a note of caution for first-time mothers and their infants, who may face a higher risk if they choose a home birth.
“I would never say women should give birth in a particular place, but hope this gives women more information to make an informed choice,” said Dr. Peter Brocklehurst, director of the Institute for Women’s Health at University College Hospital in London, one of the paper’s lead authors. He conducted the research at Oxford University.
“Birth isn’t an abnormal process, it’s a physiological process,” he said. “And if your pregnancy and labor is not complicated, then you don’t need a high level of specific expertise.”
Brocklehurst added that about 50 percent of pregnant women in England — those who are low-risk — should be able to choose where to have their baby.
More than 90 percent of pregnant women in England now give birth in a hospital. Some officials say the new study should prompt women to consider alternatives.
“This is about giving women a choice,” said Mary Newburn of NCT, a U.K. charity for parents, one of the study’s authors. She said midwife-run birth centers in England have a more homelike environment, with privacy, sofas and birthing pools.
In Britain, midwives deliver more than 60 percent of babies already. Similar care is provided in the Netherlands, where about a quarter of all births happen at home. Elsewhere in Europe, most births are led by doctors, although midwives may also be involved.
In the United States, however, less than one percent of births happen at home. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not support planned home births and warns evidence shows they have a higher risk of newborn death compared with planned hospital births. The training of midwives in the U.S. varies by state, and some have no regulations.
Brocklehurst and colleagues collected data for nearly 65,000 mothers and babies between 2008 and 2010 in England. Of those, there were 19,706 births in hospital obstetric wards, 16,840 births at home, 11,282 births in “freestanding” midwifery units — independent clinics where there are no doctors or access to anesthetics — and 16,710 births in “alongside” midwifery units, often housed within hospitals.
All the pregnancies were low-risk, meaning the mothers were healthy and carried their baby to term. Women planning C-sections or expecting twins or multiple births were excluded from the study.
In the U.K.’s hospital obstetric wards, most low-risk women don’t see a doctor during labor and are only treated by midwives.
There didn’t appear to be a difference for the infants’ health based on where the mothers planned to give birth.
But researchers found a higher risk for first-time mothers planning a home birth. Among those women, there were 9.3 adverse events per 1,000 births, including babies with brain damage due to labor problems and stillbirth. That compared with 5.3 adverse events per 1,000 births for those planning a hospital birth.
The study was published today in the medical journal BMJ.
It was paid for by Britain’s department of health and another government health research body.
Send questions/comments to the editors.


Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.