DENVER — Detectives in Denver were on the hunt for an increasingly brazen shooter.
A burglar fired through a woman’s dining room window when she threatened to call police. Ten minutes later and a mile away, someone broke into another home and shot a Bernese Mountain Dog.
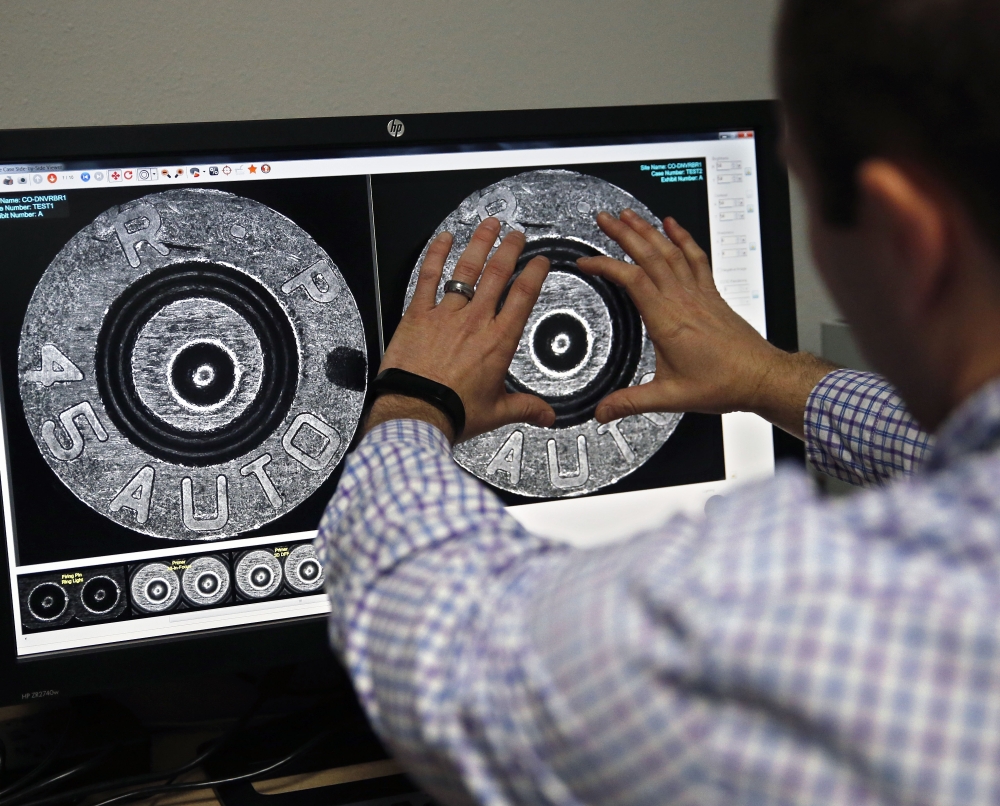
Officers scooped up the bullet casings and wondered where he would strike next.
Their break came when a witness said he was fired upon in a street fight two days later. Police gathered six more casings that were quickly entered into a national ballistics database and matched all three crimes. The evidence helped put Anthony Dennis in jail and keep him there.
STOPPING ACTIVE SHOOTERS
In many U.S. police departments, that evidence might have been shelved in an overworked crime lab, where analysts would only run it through the database to prepare a case for trial.
But authorities in Denver are leading a national trend to put ballistics evidence into the hands of investigators much more quickly – before leads dry up and suspects disappear.
“Police are beginning to understand that if you don’t quickly respond and address gun violence it can spread over space, and it can escalate much like a measles outbreak,” said Daniel Webster, director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Gun Policy and Research, which is studying whether these efforts create sustained reductions in gun violence.
Matched shell casings have helped lead to at least 35 arrests in more than 50 shootings in the two years since Denver began operating its Crime Gun Intelligence Center. At least 13 other suspects were charged with federal gun crimes, and five more had their parole revoked, according to the U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
The goal is to stop “active shooters,” people who “have already proven they have no qualms about pulling the trigger multiple times,” said Jeff Russell, supervisory special agent in the Denver ATF office. “The urgency is there to stop that person before they commit the next shooting.”
Agencies using the national database have entered nearly 2.4 million cartridge cases recovered from crime scenes, producing more than 67,000 “hits” as of February.
But there are as many as 400 million guns in circulation in the United States, and by law, the federal database was constrained from the start to include only ballistics evidence that comes from crimes. By law, test-fired shells of newly manufactured guns cannot be entered before they are sold.
DISTINCT CHARACTERISTICS
Still, with every new entry of a shell left behind by a criminal, the database becomes more robust. And when officers gather shell casings from shooting scenes as often as they can, they increase the likelihood of finding matches that provide clues to a shooter’s identity.
“It’s like the computer you have at home. If you feed it a little, it will do a little work for you. If you don’t feed it at all, it’s not going to do any work for you,” said Pete Gagliardi, a former ATF agent who is now senior vice president of Forensic Technology Inc., a private company that studies ballistics evidence.
Unlike with DNA or fingerprints that link people to crimes, this system catalogs the distinct characteristics of a firearm, not the person who used it. And the software only suggests potential hits, leaving it to analysts to verify any matches.
Denver’s early results are mixed, but promising, said Webster. The homicide rate dropped for at least five months in places where police made arrests as a result of the program, he said, although he wouldn’t provide details, since the study hasn’t been published.
Even so, it can take some convincing to put crime lab ballistics machines at the service of detectives, said George Lauder, a resident agent in charge of the ATF in Milwaukee. But soon after that city started using the technology in the immediate aftermath of shootings, investigators discovered a pattern of armed robberies based on their locations and times, he said.
“We’ve been successful in homicides where we’ve been able to identify a lead within 45 minutes,” said Lauder’s partner, Alex Kopeck. “In the past, it could have taken us months and sometimes never to identify these leads.”
Send questions/comments to the editors.


Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.